project: https://li-chongyi.github.io/Proj_Zero-DCE.html
code: https://github.com/Li-Chongyi/Zero-DCE
motivation
图像编辑软件通过调节曲线来增强图像=>image-specific 曲线估计:
根据给定图像估计pixel-wise的调整曲线。不需要任何成对或不成对的训练数据(不需要reference/GT)
图像增强=>非线性曲线映射 而不是通过image-to-image mapping
方法: non-reference loss functions
contribution
- no reference: 避免了需要paired/unpaired数据的方法中的overfitting的问题
- 设计image-specific曲线:高次、pixel-wise
- 提升人脸识别的性能
related work
传统方法
调整图像的直方图分布调整,增大图像的动态范围。
global level:
[1]. Dinu Coltuc, Philippe Bolon, and Jean-Marc Chassery. Exact histogram specification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 15(5):1143–1152, 2006.
[2]. Haidi Ibrahim and Nicholas Sia Pik Kong. Brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 53(4):1752–1758, 2007.
local level:
[3]. Chulwoo Lee, Chul Lee, and Chang-Su Kim. Contrast enhancement based on layered difference representation of 2d histograms. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(12):5372–5384, 2013.
[4]. J Alex Stark. Adaptive image contrast enhancement using generalizations of histogram equalization. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 9(5):889–896, 2000.
Retinex theory (将图像分解为reflectance和illumination,其中reflectance分量在任何光照条件下保持一致,图像质量增强任务变为illumination estimation问题):
[5]. Edwin H Land. The retinex theory of color vision. Scientific American, 237(6):108–128, 1977.
自然的信息保存方法:
[6]. Shuhang Wang, Jin Zheng, Hai-Miao Hu, and Bo Li. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(9):3538–3548, 2013.
weighted vatiation:
[7]. Xueyang Fu, Delu Zeng, Yue Huang, Xiao-Ping Zhang, and Xinghao Ding. A weighted variational model for simultaneous reflectance and illumination estimation. In CVPR, 2016.
coarse illumination map: 搜索RGB中最大intensity的pixel
[8]. Xiaojie Guo, Yu Li, and Haibin Ling. Lime: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 26(2):982–993, 2017.
考虑噪声:
[9]. Mading Li, Jiaying Liu, Wenhan Yang, Xiaoyan Sun, and Zongming Guo. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 27(6):2828–2841, 2018
自动exposure校正方法:
通过全局优化方法估计图像的S形曲线。
[10]. Lu Yuan and Jian Sun. Automatic exposure correction of consumer photographs. In ECCV, 2012.
Data-driven方法
CNN-based
一般需要pair对的数据:资源密集型(resource-intensive)。一般这种成对的数据通过 自动光照退化、改变相机的设置 采集
或者用image retouching合成
LOL数据集[Chen Wei, Wenjing Wang, Wenhan Yang, and Jiaying Liu. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement. In BMVC, 2018.] 通过改变曝光时间和ISO获取成对的low/normal光照的图像。
MIT-adobe FiveK数据集[Vladimir Bychkovsky, Sylvain Paris, Eric Chan, and Fredo ´ Durand. Learning photographic global tonal adjustment with a database of input/output image pairs. In CVPR, 2011.]包括5000raw图,每一张raw图由专家生成5个retouched图像。
[11]提出了一种估计illumination的方法:poor generalization capability
[11]. Ruixing Wang, Qing Zhang, Chi-Wing Fu, Xiaoyong Shen, Wei-Shi Zheng, and Jiaya Jia. Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation. In CVPR, 2019.
GAN-based
EnlightenGAN[Yifan Jiang, Xinyu Gong, Ding Liu, Yu Cheng, Chen Fang, Xiaohui Shen, Jianchao Yang, Pan Zhou, and Zhangyang Wang. EnlightenGAN: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision. In CVPR, 2019.]
用unpair的low/normal光照的数据。需要仔细挑选unpaired的训练数据。
methods
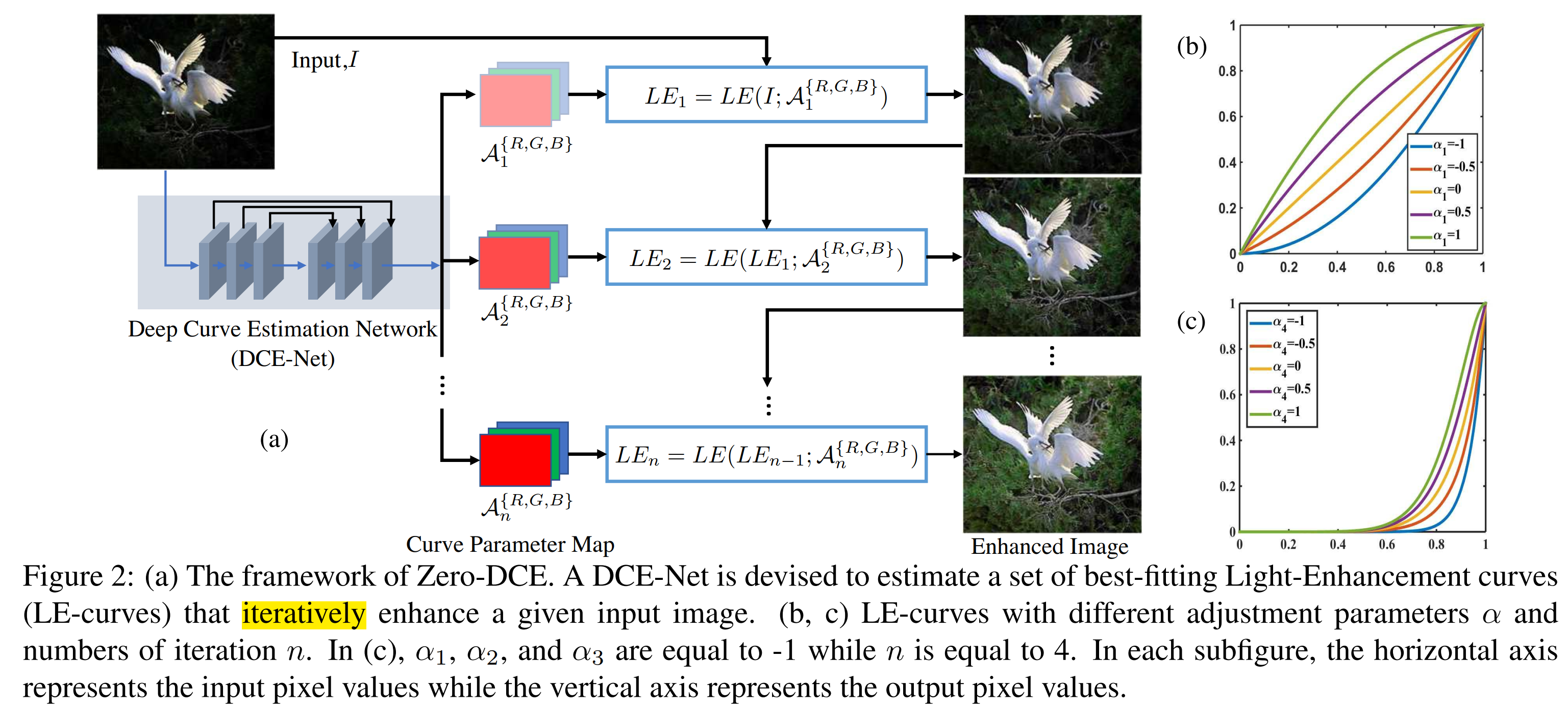
通过non-reference loss function实现不需要paired/unpaired的数据。通过迭代训练得到结果。
Light-enhancement curve
自适应的曲线参数只由输入图像决定。曲线要是单调的来保持周围像素的区别。曲线要处处可微保证可以梯度反传。
其中$\alpha \in [-1,1]$, 将LE曲线分别作用于R\G\B通道,而不仅仅作用于illumination通道。调节3个通道可以更好的保持固有的色彩,减少过饱和。
上式可以多次迭代,写为:
其中n为迭代次数,他们设为8. 多次迭代有更强的调节能力。
但是如果$\alpha$在每一个点是固定值,只能是全局调节。全局调节容易带来over-/under- enhance local区域。为了解决这个问题,他们将$\alpha$设置为pixel-wise的参数。上式变为:
其中A是一个与原图等大小的parameter map。
假设,一个局部区域的像素点有相同的intensity. 所以输出图像里的相邻像素也有单调的关系。
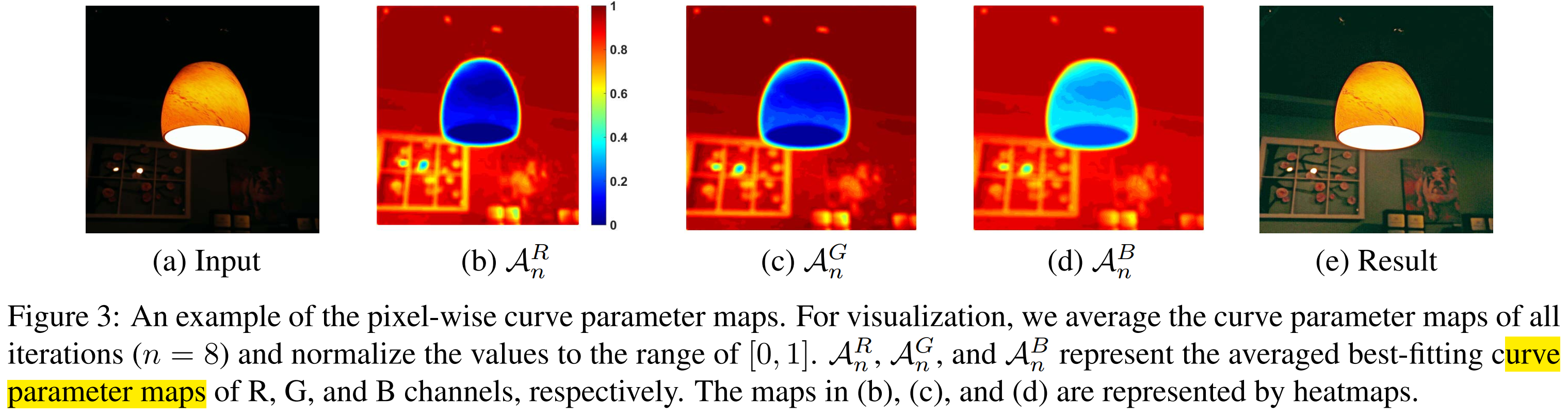
DCE-Net(具体结构见补充材料)
- 输入:低光照图像
- 输出:pixel-wise的高阶curve参数图。8次迭代共24个parameter maps
- 网络细节:不包括down-sampling和BN,它们会丢失相邻像素的关系。最后一层conv接Tanh
1. spatial consistency loss
使增强后的图像保持时域的连贯性(coherence)
$K$为局部区域数,$\Omega(i)$为4个相邻区域(上下左右)。Y和I是局部区域的平均强度值(intensity)。局部区域的大小设为4*4. 相当于对K个4*4的局部区域,要求enhance前后图的局部区域与其邻域的强度差,差不多。
2. exposure control loss
控制曝光的程度。测量局部区域的平均强度与well-exposedness的级别E之间的距离。E=0.6、在[0.4,0.7]之间差不多。
M代表M个16*16的没有overlap的局部区域,Y是enhanced图像中局部的平均强度值。
3. color constancy loss
校正色彩偏差。
其中,$J^p$代表enhanced图像p channel的平均强度。
4. illumination smoothness loss
保持相邻pixel的单调性。对每个curve参数图A有:
N为迭代次数。求梯度的操作有点像TV loss。
total loss
$W_{col}=0.5,W_{tv\mathcal{A}}=20$.
ablation

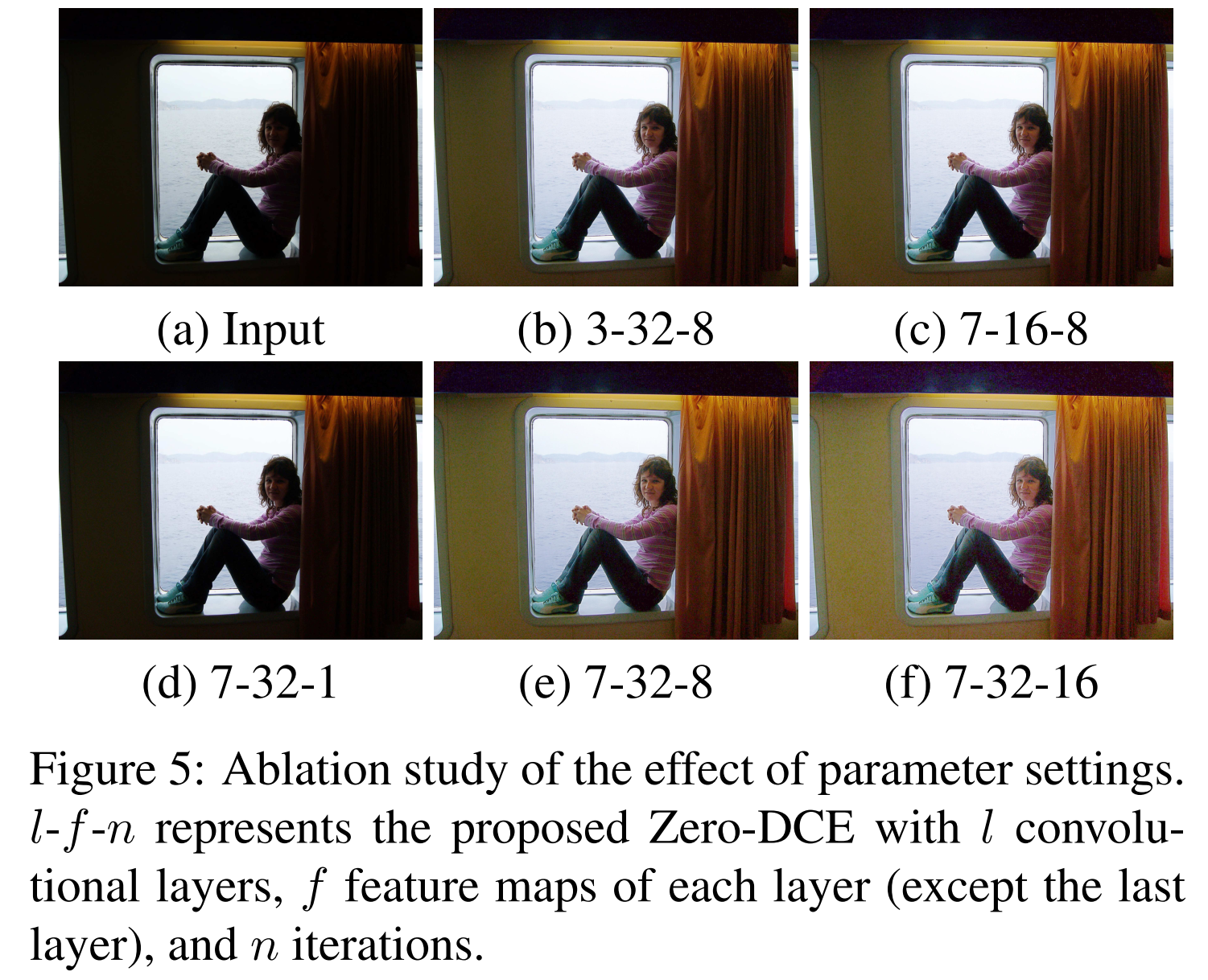
训练数据:用multi-exposure的训练数据更好。
benchmark results
no reference 结果(US/PI)
视觉评判标准:
1) whether the results contain over-/under-exposed artifacts or over-/under enhanced regions;
2) whether the results introduce color deviation;
3) whether the results have unnatural texture and obvious noise.
指标:
user study (US) score
non-reference perceptual index (PI)
[Yochai Blau and Tomer Michaeli. The perception-distortion tradeoff. In CVPR, 2018.]
[Chao Ma, Chih-Yuan Yang, Xiaokang Yang, and MingHsuan Yang. Learning a no-reference quality metric for single-image super-resolution. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 158:1–16, 2017.]
.png)
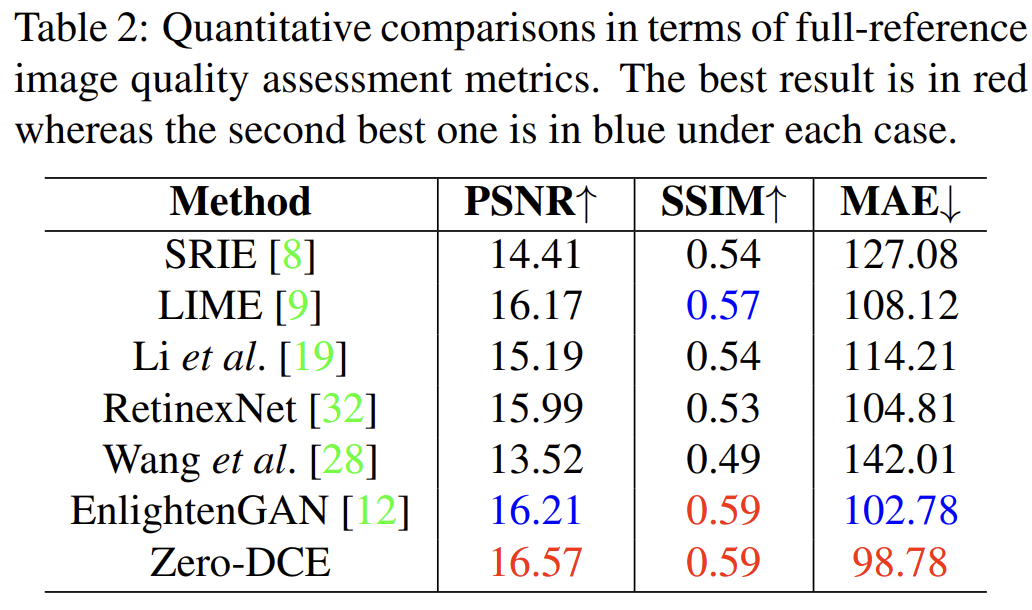
full reference 结果(PSNR/SSIM)
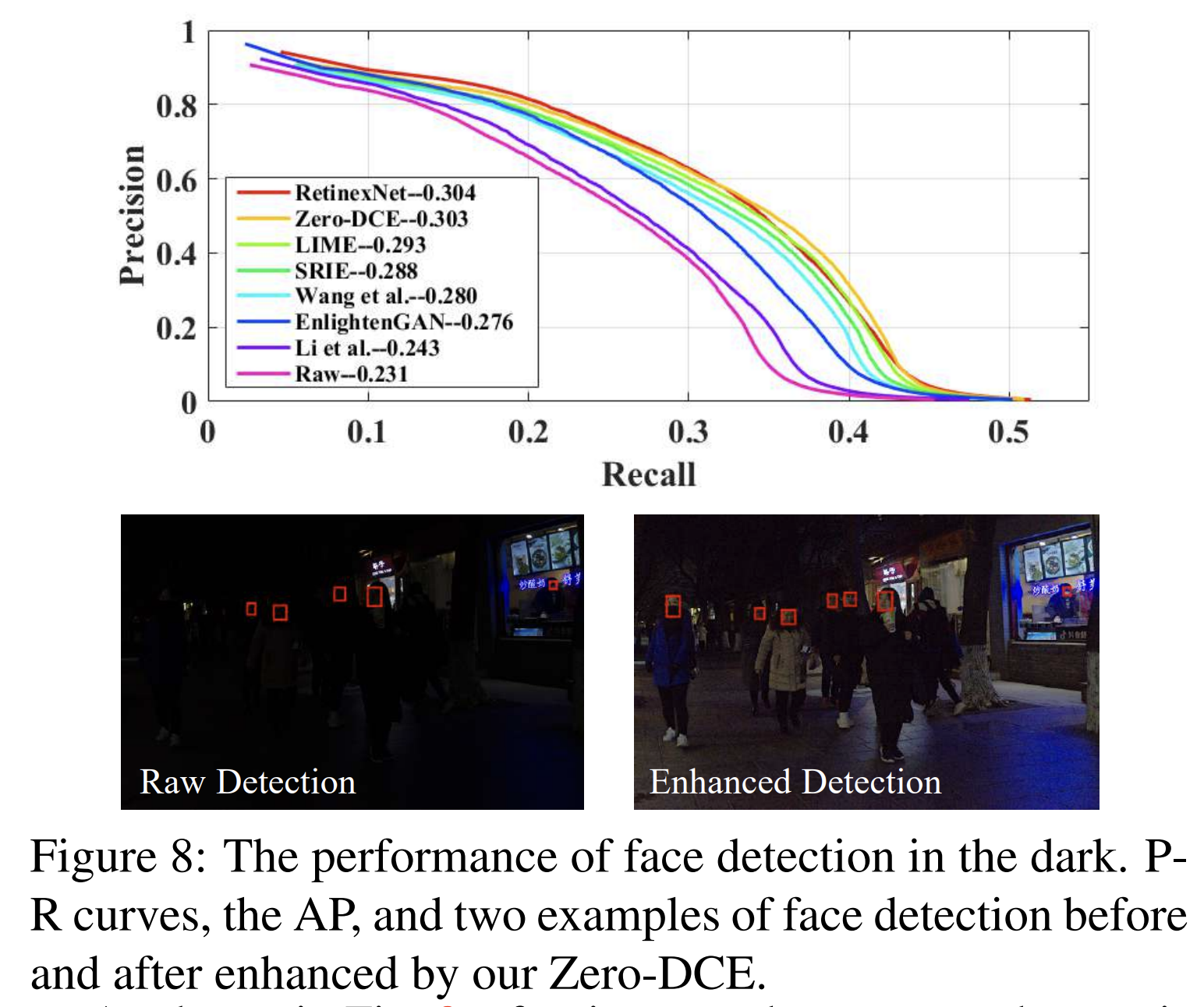
face detection
用SOTA的face detector(DSFD: https://github.com/Ir1d/DARKFACE_eval_tools )
将不同enhance方法得到的图送入DSFD,得到P-R curve。